Harvard Natural Sciences Lecture Demonstrations
1 Oxford St Cambridge MA 02138 Science Center B-08A (617) 495-5824
enter search criteria into the search box
Key to Catalog Listings
Size: from small [S] (benchtop) to extra large [XL] (most of the hall)
Setup Time: <10 min [t], 10-15 min [t+], >15 min [t++] /span>
Rating: from good [★] to wow! [★★★★] or not rated [—]
Copyright © 2024 The President and Fellows of Harvard College | Accessibility | Digital Accessibility | Report Copyright Infringement
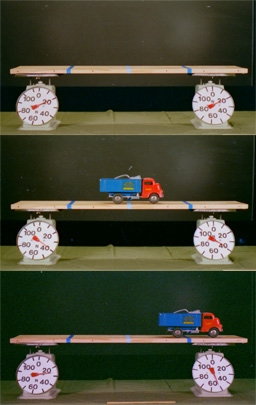 Beam supported at ends with platform scales and toy truck as load to demonstrate moment arms.
Beam supported at ends with platform scales and toy truck as load to demonstrate moment arms.